Remote Homology Detection using enriched databases
Designed protein-like intermediate sequences fill-in the sparse regions in protein sequence space and aid in remote homology detection searches.
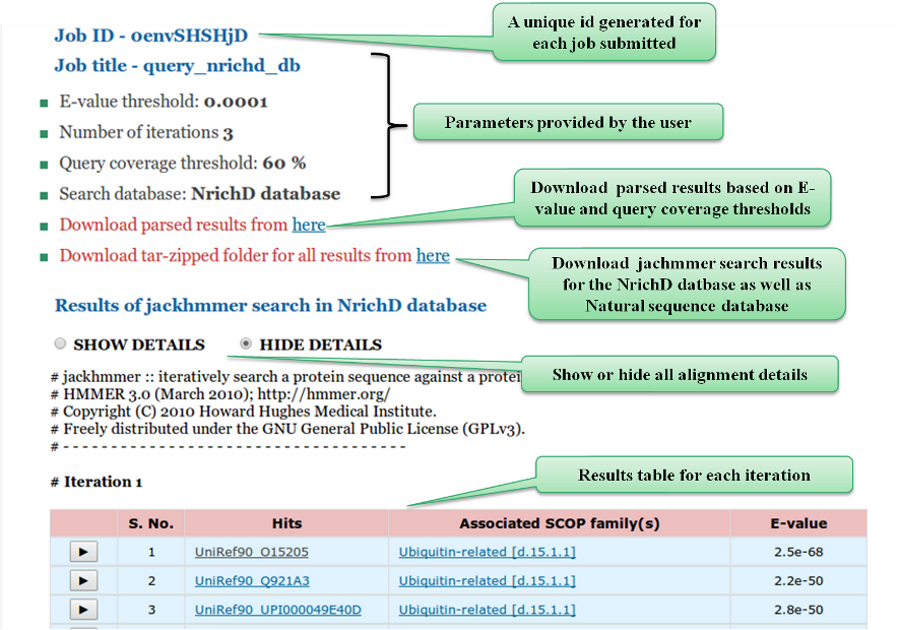
The results page describes the parameters defined by the user, followed by the results of
jackhmmer searches performed in the NrichD and Natural sequence databases. We also provide a link to the
user to download parsed results as well as the raw results file. The jackhmmer results are displayed in a tabular
form. The details of each hit such as Query description, Hit description, % Identity, % Similarity and E-value along
with the alignments are displayed below using a toggle switch.
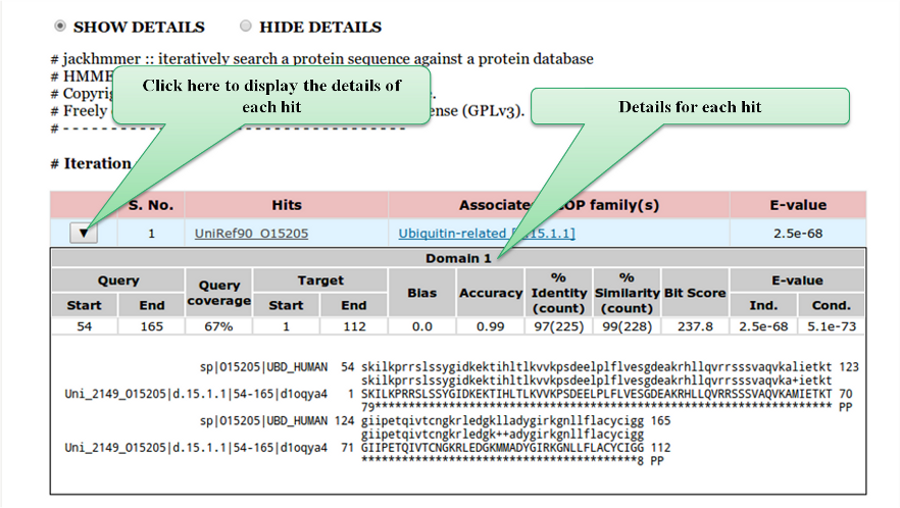
Query start/end - The start/end of the query domain observed in pairwise sequence alignment.
Target start/end - The start/end of the target(hit) domain observed in pairwise sequence alignment.
Query coverage - Percentage coverage of query sequence in the alignment.
Bias - The bias composition correction (ranging between 0 and 1). Lower the better.
Accuracy - Measure of reliability of the overall alignment. The accuracy ranges from 0 to 1, with 1.00 indicating a completely reliable alignment.
% Identity (count) - The percentage of identical residues between the query and target. The query length is taken as the denominator. The number in brackets is absolute count.
% Similarity (count) - The percentage of similar residues between the query and target. The query length is taken as the denominator. The number in brackets is absolute count.
Independent E-value - Statistical significance of sequence in the whole database search.
Conditional E-value - Statistical significance of each domain given that it has already been decided that the target sequence is a true homolog.
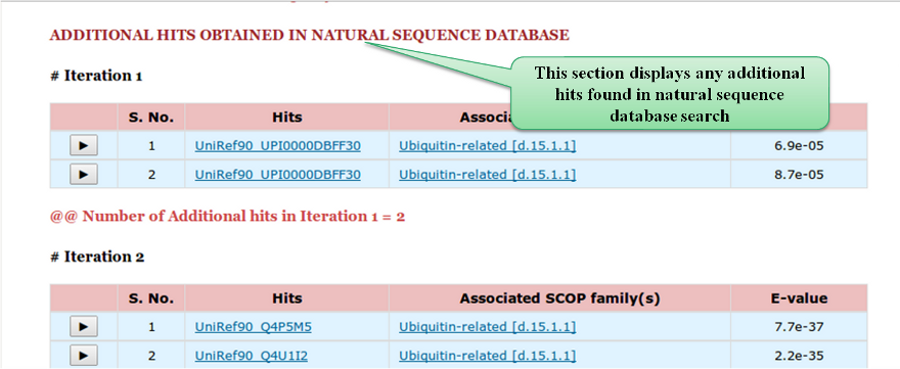
Following the results for NrichD database search, we also report additional hits (if any) observed in
jackhmmer searches within natural sequence database.
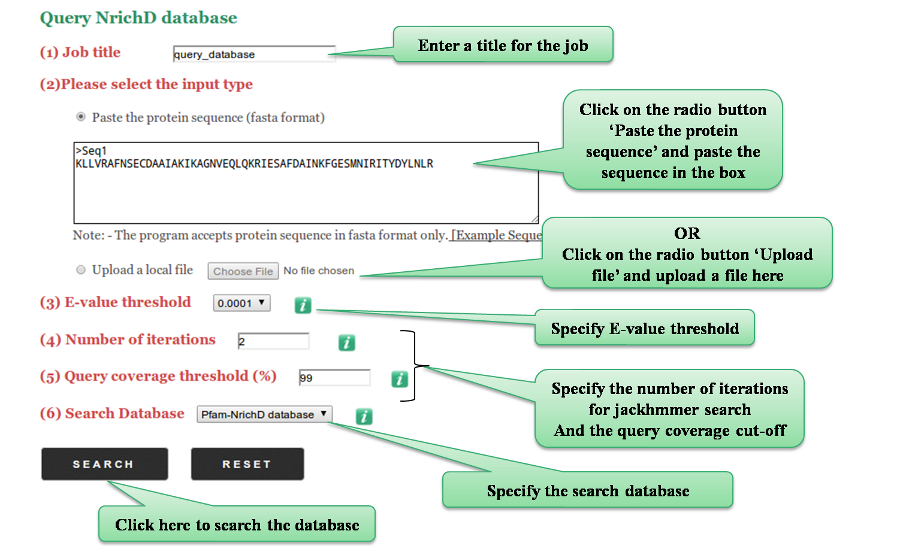
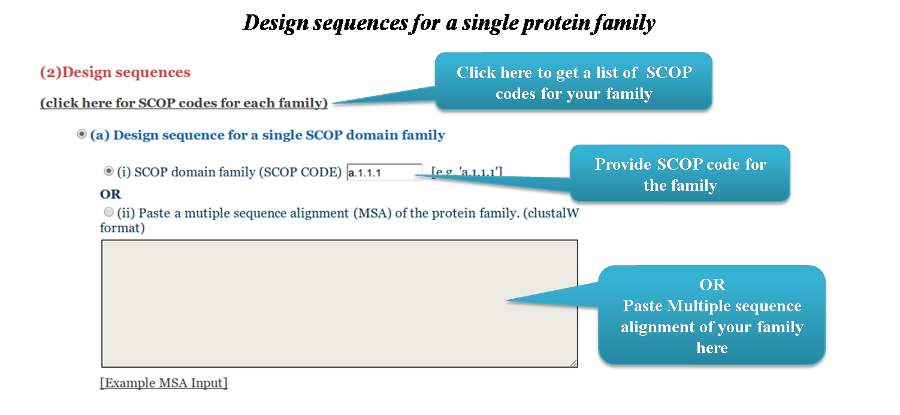
If the user chooses to design sequences for a family, they can provide the SCOP domain family code OR alternatively submit a multiple sequence alignment of their protein family in ClustalW/Stockholm format.
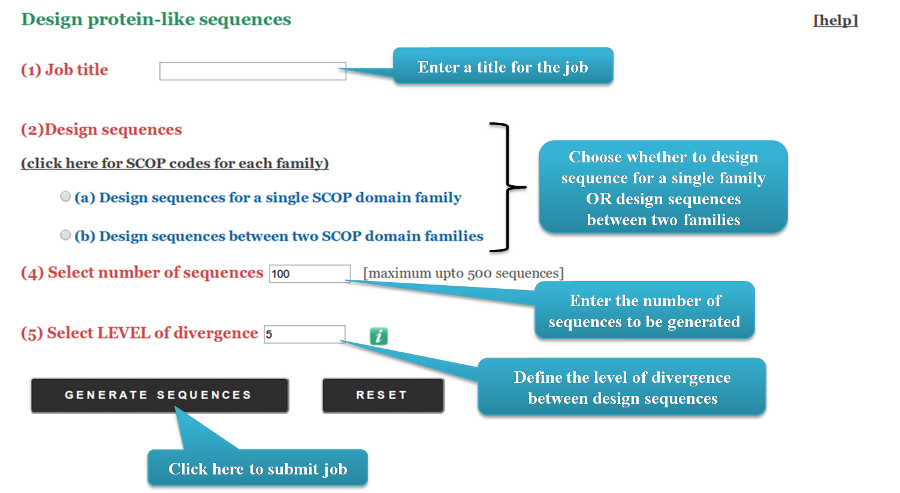
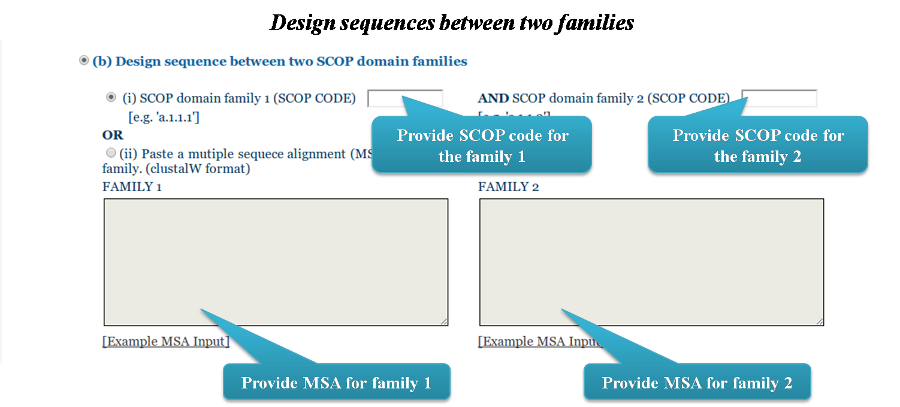
The user can also choose to design sequences between two families belonging to the same fold.
They can either provide the SCOP domain family codes for the two families OR provide an MSA for both families.
The list of SCOP domain families can be obtained from here
Please note: There are various important criteria that we have employed in the design process.
First and the foremost check in the design of intermediate sequences is that the alignment length between the two parent
profiles should be at least 80% length of the smaller family. This check is not required if designing sequences for a single family.
Secondly, once artificial sequences are generated at the defined level, they are validated by their ability to detect their parent
profiles in RPS-BLAST searches at E-value better that 0.0001 and 80% coverage of the artificial sequence. If the user has provided
an MSA for the protein family or families, these sequences are appended to the validation database (SCOP database, Astral 95) and
PSI-BLAST searches are performed in this database. If the artificial sequences are able to detect sequences in the parent family
or families at E-value better than 0.0001 and 80% query coverage, they are called designed sequences.
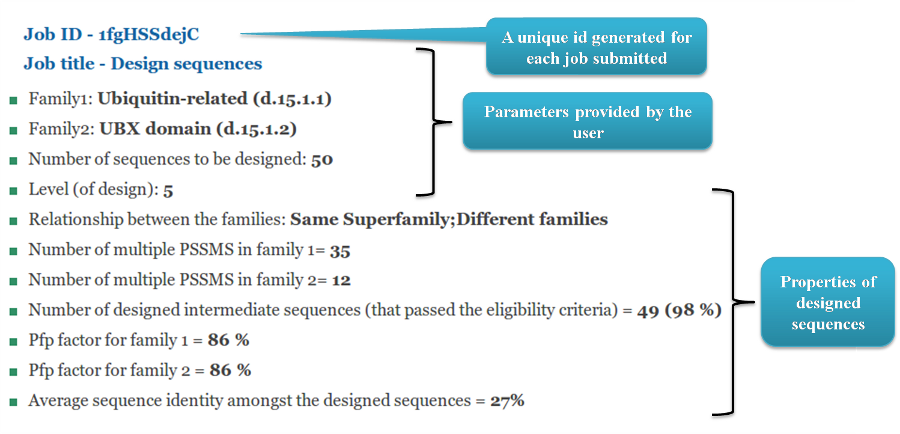
The results page for 'Design protein-like sequences' firstly describes the defined parameters
given by the user. It then describes the properties of the sequences that passed the eligibility criteria. We report the number
and percentage of designed artifical sequences that pass the eligibility criteria. If the user defines SCOP domain
family codes then we also report the average Pfp factor which denotes the percentage of total profiles detected for the
protein family other than the parent profiles.
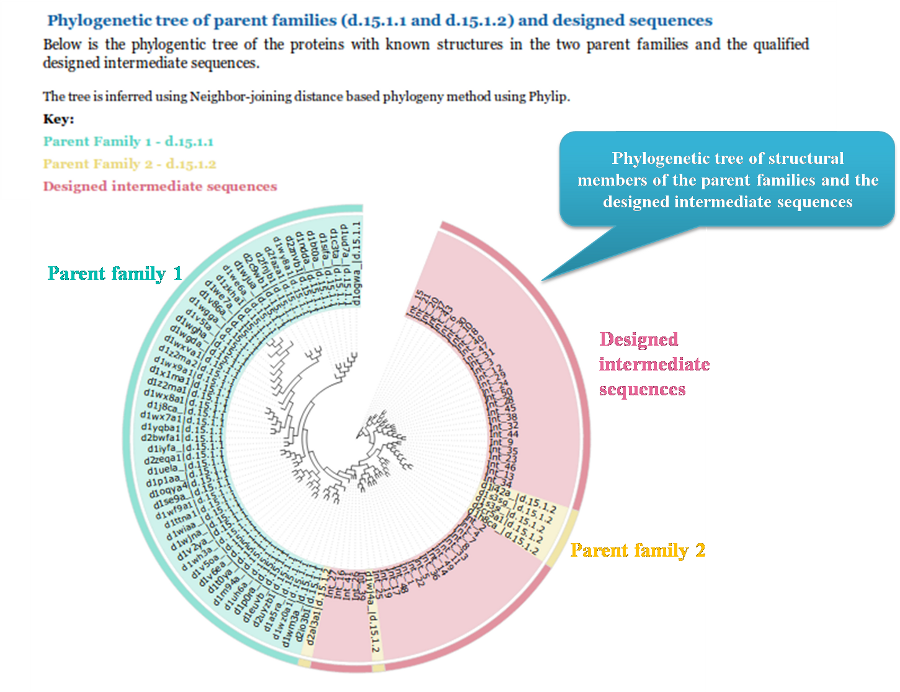
We then display a phylogenetic tree between the structural members of the parent family(ies) and the designed sequences. The
designed sequences are shown in pink and family 1 and family 2 are depicted in sea-blue and wheat color respectively.
The phylogentic tree is inferred from using Neighbor-joining distance based method using Phylip tool.
The tree and the multiple sequence alignment between the parent families and designed sequences is available
for download.
Further, a link is provided to download the artificial sequences that passed all criteria (designed
sequences). The user can also download a multiple sequence alignment of all these designed protein-like sequences.
Lastly the page displays all the designed sequences.
Intermediate sequences are annotated as 'Int'. The annotation line also includes the families involved
in the design process. These two families are pipe-separated. It also indicates the level at which the sequences were
designed.
Please note: The final number of designed protein-like sequences may be less than or equal to the defined number of
sequences given by the user. This may occur because not all artificial sequences pass the eligibility criteria.